AI Emotion Recognition, or Affective Computing, enables machines to interpret human emotions through facial expressions, voice tones, and text analysis. It enhances customer service, mental health support, gaming, education, smart homes, and security. Companies like Affectiva, Microsoft, and IBM leverage this technology for innovation. AI-driven emotion recognition is transforming human-computer interactions across industries.

In 1956, John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky founded Artificial Intelligence after being astounded by how fast a machine could solve very difficult problems for humans. As it turns out, programming an AI to comprehend and mimic emotions is much harder than teaching it to perform logical tasks like chess.
“After 60 years of AI, we have now accepted that the things we initially thought were easy are actually very hard, and what we thought was hard, like playing chess, is very easy,” says Alan Winfield, a robotics professor at UWE in Bristol.
Social and emotional intelligence is innate in human nature. We interpret emotions automatically and respond appropriately. We are guided in how to act in various situations by this basic level of intelligence, which we have developed over time via various life experiences. Can a machine be taught this automatic understanding? Let’s understand how AI development has evolved itself in Emotional AI in the blog below.
“Emotion AI,” also known as “Affective Computing,” is a component of artificial intelligence that’s been around us since 1995. It understands, interprets, and even replicates human emotions via facial expressions, voice tone, and psychological signals. These systems improve emotional intelligence and human-computer interaction by combining methods like speech recognition and neural networks.
The majority of AI emotion recognition systems currently in use examine a person’s voice, facial expressions, and any written or spoken words. For example, AI integration into systems might determine that someone is in a good mood if the corners of their mouth are up, but a wrinkled nose indicates disgust or rage.
Similarly, a shaky, high voice and rushed speech can be signs of fear, but a shout of “cheers!” is most likely an expression of joy. More sophisticated systems, in addition to speech and facial expressions, also analyze gestures and even the environment. A person who is made to smile at gunpoint is probably not thrilled, and such a system acknowledges that.
AI emotion recognition systems use vast amounts of labeled data to learn the relationship between an emotion and its outward expression. The information could include TV show audio or video recordings, real-life interviews and experiments, movie or theater snippets, and professional actors’ dialogue.
Depending on the goal, photos or text corpora can be used to train simpler systems. For instance, using photos, this Microsoft project attempts to infer a person’s gender, emotions, and approximate age.
AI emotion recognition is a concept that reflects human emotional intelligence. It includes AI machines’’ natural and sympathetic perception, interpretation, and reaction to human emotions. Some applications of this technology include, customer service, mental health support, and human-computer interaction depend on the ability to recognize emotions.
This technology allows AI to provide personalized responses, improve user experiences, and even insights into mental health. It has long been a lofty objective for artificial intelligence researchers to give machines emotional intelligence.
In many AI emotion recognition fields, integrating AI development services can help identify and comprehend emotions that could have a significant impact on how systems relate to and interact with people.
AI emotion recognition is revolutionizing how machines understand human feelings. It decodes faces, voices, and texts, transforming how machines understand and respond to our feelings in real-time.
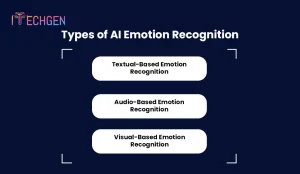
Let’s discuss the three types of artificial emotion recognition:
Text-based emotion recognition uses machine learning and artificial neural networks to analyze textual data and extract emotional information. Conventional methods use knowledge-based systems with sizable labeled datasets for statistical models that demand broad emotional vocabularies.
A substantial amount of textual data expressing human affect has been produced by the growth of online platforms. Semantic analysis is used by tools like WordNet Affect, SenticNet, and SentiWordNet to identify emotions. Emotionally intelligent computers can now perform end-to-end sentiment analysis and detect minute emotional nuances in text thanks to deep learning models, which have further advanced this field.
The latest research has introduced state-of-the-art techniques like emotion-enriched word representations and multi-label emotion classification architectures. This has enhanced the system’s capacity to identify emotional states and take cultural differences into account.
Affective computing systems analyze and categorize emotions in text across a variety of applications, including emotional experience in art and commerce, by using benchmark datasets from sources like tweets or WikiArt.
In audio emotion recognition, systems use acoustic features like pitch, tone, and cadence to study human affect in speech signals. While classifiers like Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and Support Vector Machines (SVMs) process this data to find emotional cues, affective wearable computers with audio sensors use tools like OpenSMILE for feature extraction.
Deep learning advances train convolutional neural networks (CNNs) directly on unprocessed audio data, removing the need for human feature engineering. These networks improve performance by capturing both the spectral and temporal aspects of speech, which helps build emotionally intelligent computers that react sensibly and engage with users in a natural way.
Visual-based emotion recognition—which uses computer vision and facial recognition technologies—focuses on recognizing human emotions from facial expressions and other visual stimuli. Algorithms that can identify emotional states from facial expressions, movements, and other modalities are trained using datasets such as CK+ and JAFFE.
Elastic bunch graph matching is one technique that dynamically analyzes facial deformations across frames, and attention-based modules help to improve focus on important facial regions. Methods like local binary patterns (LBP) and auto-encoders extract textural and spatial features, which helps systems better comprehend human emotions.
Human affect recognition has been improved by research into fleeting micro-expressions, and involuntary facial movements that reveal hidden emotional cues. These discoveries can be combined to create effective technologies that can simulate emotions and provide truly intelligent responses in human-machine interactions.
“The emotion AI market is projected to grow from USD 2.74 billion in 2024 to USD 9.01 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 21.9% during the forecast period.”
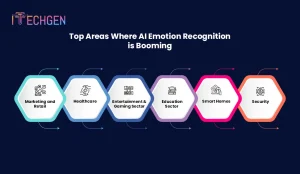
Artificial Emotion Recognition has a broad spectrum of use cases across various industries. It greatly impacts how services are delivered and improves the user experience. Here are some of the key areas where artificial Emotion Recognition is making a difference.
AI Emotion Recognition provides enterprises with useful insights into customer behavior, allowing them to customize or reshape their marketing strategies.
Enhance customer experiences, improve security, and revolutionize industries with AI emotion recognition. Stay ahead with cutting-edge AI solutions.
Artificial Emotion Recognition has introduced significant benefits in the healthcare sector in terms of patient interaction and care.
Mental health monitoring: By analyzing the facial expressions of a patient over a period of time, doctors and specialists can identify symptoms of anxiety or depression.
Pain management: It can also measure the amount of pain in patients who might not be capable of expressing themselves clearly, such as those in critical care or recovering from surgery.
Quick Read: The Cost of Implementing AI in Healthcare
AI’s ability to identify user emotions allows immersive experiences and personalized content recommendations in the entertainment and gaming industries.
Customized Content: In the entertainment sector, AI-powered systems employ emotion analysis to suggest content that is specifically suited to each user. This entails recommending games that align with players’ emotional preferences. It means creating playlists or movie choices for music and movie streaming services that speak to the user’s current emotional state, whether they are looking to unwind or energize themselves.
Improving Immersion: AI in the gaming sector increases player immersion by adjusting game dynamics to their emotional responses. For example, if a player seems disinterested or bored, the game may add new tasks or features to keep them interested. This flexible strategy maintains players’ active participation and improves immersion.
AI Emotion Recognition Technology is also advancing in the field of education by helping to customize learning experiences to students’ emotional states.
Student Engagement: Teachers can leverage AI Emotion Recognition to track student engagement and modify their lesson plans and content to keep them engaged, focused, and motivated.
E-Learning Platforms: By incorporating AI Emotion Recognition, online learning platforms can dynamically modify content and learning paths in response to learners’ emotional cues, potentially enhancing satisfaction and results.
AI Emotion Recognition in smart home settings can improve communication between inhabitants and their living areas, increasing the responsiveness and sensitivity of homes to their emotional needs.
Automated Modifications – AI Emotion Recognition-enabled smart home systems can change the music, lighting, and temperature according to the residents’ moods, resulting in a more cozy and encouraging space.
Elderly Care – Smart homes with emotion recognition power can keep an eye on the emotional health of senior citizens and identify signals of distress or confusion, allowing caregivers to provide support and assistance.
AI emotion recognition allows security systems to recognize and interpret human emotions in case of fear, threat, or distress. It enables faster and more accurate responses to potential dangers:
Threat Detection – Integrating AI emotion recognition into security systems can help identify individuals displaying suspicious or aggressive emotions, potentially preventing crimes before they occur. This application is particularly useful in crowded public spaces like airports and malls, where the ability to quickly assess emotional states can enhance overall security.
Understanding human emotions in businesses is being enhanced by AI Emotion Recognition, which can analyze voice tones and detect subtle facial expressions. These are the leading companies using this state-of-the-art technology to spur innovation and revolutionize sectors.
| Company | Example Business Applications |
| Affectiva | Emotion detection through facial expressions and voice analysis for automotive and marketing. |
| Realeyes | Emotion recognition for marketing optimization and audience engagement. |
| Kairos | Facial recognition and emotion analysis for customer service and access control. |
| Sightcorp | Visitor insight and customer analytics using facial emotion recognition. |
| Cogito | Voice sentiment analysis for customer service optimization and healthcare. |
| Microsoft Corporation | Emotion recognition via Azure AI, including facial expression analysis and sentiment detection. |
| Amazon (AWS) | Emotion detection using Amazon Rekognition for image and video analysis. |
| Emotion recognition through Google Cloud AI, including sentiment analysis in text and voice. | |
| IBM | Emotion detection using IBM Watson, including facial and voice emotion analysis. |
AI integration is beyond technological advancement. This game-changer supports businesses in establishing stronger and long-term relations with their customers. From marketing and retail to healthcare, education, and entertainment, AI has spread its wings in various forms. One of them is AI emotional recognition. The technology bridges the gap between empathy and technology by comprehending and reacting to human emotions, resulting in more profound and significant customer experiences.
At iTechGen, it takes pride in being a part of AI business solutions and related technologies. We help organizations in building modern AI applications, including AI emotion recognition, that enhance user experience and nurture user engagement. Our team always strives to keep pushing the boundaries of what’s feasible. Reach out to our AI development company to employ artificial Emotion Recognition in your business today.
AI integration is beyond technological advancement. This game-changer supports businesses in establishing stronger and long-term relations with their customers. From marketing and retail to healthcare, education, and entertainment, AI has spread its wings in various forms. One of them is AI emotional recognition.

Pankaj Arora is the Founder & CEO of iTechGen, a visionary leader with a deep passion for AI and technology. With extensive industry experience, he shares expert insights through his blogs, helping businesses harness the power of AI to drive innovation and success. Committed to delivering customer-first solutions, Pankaj emphasizes quality and real-world impact in all his endeavors. When not leading iTechGen, he explores emerging technologies and inspires others with his thought leadership. Follow his blogs for actionable strategies to accelerate your digital transformation and business growth.
View More About Pankaj Arora